Civil Engineering 2019
PAST CONFERENCE REPORT
The International Conference on Structural and Civil Engineering Research (CIVIL ENGINEERING 2018) hosted through EuroSciCon took area at Hyatt Place, Amsterdam, Netherlands all through October 01-02, 2018. It was once organized via EuroSciCon and generous response used to be obtained from the Editorial Board Members of EuroSciCon Journals as well as from eminent scientists, gifted researchers, and young scholar community. Researchers and students who attended from one of a kind parts of the world made the convention one of the most successful and productive activities in 2018 from EuroSciCon. The two-day application witnessed thought-provoking keynote and plenary presentations from professionals in the subject of Structural and Civil Engineering Research, highlighting the theme, "Advance Technologies in Structure and Civil Engineering".
The meeting used to be carried out through a number sessions, in which the discussions have been held on the following major scientific tracks:
- Civil Engineering and Architecture
- Steel Structures and Construction
- Earthquake Engineering and Disaster Management
- Structural Analysis and Designing
- Reinforced Concrete Structure
- Building Technology and Construction Management
- Modular Constructions
The highlights of the meeting were from the eminent keynote lectures from:
Civil Engineering 2018 Conference performed a vital role in promoting multidisciplinary interactions between Structural and Civil Engineering Research to decorate lookup in Civil Engineering. The software covered cutting-edge and emerging lookup innovations in the discipline of Civil Engineering.
We would mainly thank our Moderator for his contribution to the conference.
We definitely thank the Organizing Committee Members and the Editorial board of Civil Engineering 2018 Conference for their gracious presence and continuous aid for the duration of the lawsuits of this event. With the precious feedback and beneficent response obtained from the contributors of the event, EuroSciCon would like to announce the commencement of “International Conference on Structural and Civil Engineering Research” at some stage in June 06-07, 2019 in Paris, France with the theme: “Engineering for Sustainable Infrastructure & Development”.
Let us meet once more @ Civil Engineering 2019
Welcome Message
For the benefit of the Structural and Civil Engineering Research Conference 2019 Organizing Committee, we anticipate inviting you to Paris, France. The world focused on the field of Civil and Structure Engineering, this is your most opportunity to accomplish the greatest gathering of individual from the overall advancement undertakings. With the members from around the globe focused on learning about recent and advanced Civil Engineering Researches.
Coordinate shows, fitting information, meet with present and potential steel merchants, make a sprinkle with another item offering, and get name affirmation at this 2 days event. Unbelievably renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, systems, and the most current updates in Structural and Civil Engineering fields are indications of this social occasion.
It will provide scope to student to meet and interact with international speakers and professors, CEOs. This meeting joins masters, researchers, analysts and understudies from all locales of Civil Engineering, Architectural, Structural Engineering and other related civil engineering affiliations, steel merchants, building and improvement specialists, Developers, Contractors, Interior Design, Consultancy, Building Material creators of national importance. The Organizing Committee ceaselessly attempts to make what we believe is a remarkable specialized program at an extraordinary esteem.
We believe you will present a theoretical displaying of your most recent research or undertaking victories, and that you will take full preferred standpoint of the specialized sessions exhibited by your associates who have as of now liberally volunteered their chance and ability. This is likewise your chance to interface with condition of-the-hone experts and to reconnect with your companions and associates. Set aside opportunity to survey the Advanced Program. You'll see that the 2019 Conference program will offer new and improved proficient tracks, board discourses, superb keynote speakers and arranged strolling visits, among different exercises.

Much thanks to you for taking an interest in the Structural and Civil Engineering Research Conference 2019. We anticipate your introductions and comrade. We hope to see you at Paris.
About Conference
EuroSciCon warmly welcomes to all the experts in the field of Structural and Civil Engineering to attend its upcoming conference on Structural and Civil Engineering Research, to be held during June 06-07, 2019 in Paris, France. The Conference is based on the Theme: Engineering for Sustainable Infrastructure & Development. Civil Engineering 2019 Conference will make the perfect platform for global networking as it brings all together speakers, renowned speakers, business persons , CEO’s , across the globe to most exciting and memorable event ,with interactive sessions, poster presentation, world class exhibition. Advances in the field of Construction and Structures are one of the crucial factors in the economic powers of the developed countries and developing countries.
This is 2-days Meeting and you can participate in a number of educational formats including General Sessions, Poster Presentations, and Workshops/Symposium, Meet-the-Professor Sessions, Oral Presentations and other interactive and informal exchanges.
We hope you to see in Structural and Civil Engineering Research Conference 2019 at Paris.
OPPURTUNITIES FOR ATTENDEES
For Researchers & Faculty:
- Speaker Presentations
- Poster Display
- Symposium hosting
- Workshop organizing
For Universities, Associations & Societies:
- Association Partnering
- Collaboration proposals
- Academic Partnering
- Group Participation
For Students & Research Scholars:
- Poster Competition (Winner will get Best Poster Award)
- Young Researcher Forum (YRF Award to the best presenter)
- Student Attendee
- Group registrations
For Business Delegates:
- Speaker Presentations
- Symposium hosting
- Book Launch event
- Networking opportunities
- Audience participation
For Companies:
- Exhibitor and Vendor booths
- Sponsorships opportunities
- Product launch
- Workshop organizing
- Scientific Partnering
- Marketing and Networking with clients
EuroSciCon organizes International Civil Engineering Meetings annually across Europe, Austria, Ireland, Germany, France, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Finland, Luxembourg, Hungary, Italy, Norway, Poland, Denmark, Macedonia, Greece, Portugal, Romania, Czech Republic, Switzerland, United Kingdom, Belgium, Scotland, Latvia, Ukraine, Sweden, Denmark, Spain, Netherlands Russia, Bulgaria, France, with solitary subject of quickening logical revelations.
Topics:
Civil Engineering and Architecture
Structural and Construction Engineering
Building Technology and Construction Management
Steel Structures and Construction
Structural Analysis and Designing
Earthquake Engineering and Seismic Risk Mitigation
Transportation and Traffic Engineering
Water Resource Engineering and Technology
Sustainability & Green Structures
Materials Science and Engineering
Tunnel Engineering and Construction
Designing of Special Structures and Concrete Technology
Construction Market Research and Industry Analysis
Who should attend?
Engineers who are specialized on the specific fields like Civil engineers, Structural Engineers, Mechanical Engineers (To Present Their case reports and to update their Knowledge at the conference), Civil industry professionals, Building services engineer, Building control surveyor, Environmental engineers who are related to that topics. Bridge Construction Industries, Renewable Energy Industries, Software Publishing Houses specializing in Construction Design software’s are the Potential Exhibitors for the Respective Conferences. Civil Engineering associations, Earthquake Engineering Research Institutes, Institutions of Civil Engineering Surveyors, Institutions of Transportation Engineers; Students and Delegates in related areas.
Why to attend??
With members from around the world focused on the field of Civil Engineering; this is your single best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the global Civil Engineering Industries. Conduct demonstrations, distribute information, meet with current and potential civil traders, make a splash with a new product line, and receive name recognition at this 2-days event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, tactics, and the newest updates in Civil Engineering fields are hallmarks of this conference. Conference brings together experts, researchers, scholars and students from all areas of Civil Engineering, Architectural, Structural Engineering, Geo-Technical, Environmental and other related areas, Civil associations, civil traders, building and construction professionals, Developers, Contractors, Interior Design, Consultancy, Building Material manufacturers.
About Paris:
Paris, France's capital is a major European city and a global center for art, fashion, gastronomy and culture. Its 19th-century cityscape is crisscrossed by wide boulevards and the River Seine. Beyond such landmarks as the Eiffel Tower and the 12th-century, Gothic Notre-Dame cathedral, the city is known for its cafe culture and designer boutiques along the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré.

The City of Paris's administrative limits form an East-West oval centred on the island at its historical heart, the Île de la Cité; this island is near the top of an arc of the river Seine that divides the city into southern Rive Gauche (Left Bank) and northern Rive Droite regions. Paris is the core of a built-up area that extends well beyond its limits: commonly referred to as the agglomération Parisienne, and statistically as measure of urban area, the Paris agglomeration's 2013 population of 10,601,122 made it the largest urban area in the European Union. City-influenced commuter activity reaches well beyond even this in a statistical aire urbaine de Paris (a measure of metropolitan area), that had a 2013 population of 12,405,426, a number one-fifth the population of France, the largest metropolitan area in the Eurozone.
Sessions and Tracks
Track 1: Civil Engineering and Architecture
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the outline, development, and upkeep of the physical and normally constructed condition, including works like streets, spans, trenches, dams, airplane terminals, sewerage frameworks, pipelines and railways. Civil engineering is customarily broken into various sub-disciplines. It is the second-most established designing order after military engineering, and it is characterized to recognize non-military building from military engineering. Civil engineering happens in general society division from city through to national governments, and in the private part from singular property holders through to universal organizations.

There are a number of sub-disciplines within the broad field of civil engineering. General civil engineers work closely with surveyors and specialized civil engineers to design grading, drainage, pavement, water supply, sewer service, dams, electric and communications supply. General civil engineering is also referred to as site engineering, a branch of civil engineering that primarily focuses on converting a tract of land from one usage to another. Site engineers spend time visiting project sites, meeting with stakeholders, and preparing construction plans. Civil engineers apply the principles of geotechnical engineering, structural engineering, environmental engineering, transportation engineering and construction engineering to residential, commercial, industrial and public works projects of all sizes and levels of construction.
- Pavement and drainage design
- Dam Construction
- Water supply
- Electric and communications supply
- Sewer service
Track 2: Structural and Construction Engineering
Structural engineering is concerned with the structural outline and structural examination of structures, spans, towers, flyovers (bridges), burrows, seaward structures like oil and gas fields in the ocean, aero-structure and different structures. This includes distinguishing the heaps which follow up on a structure and the powers and stresses which emerge inside that structure because of those heaps, and afterward designing the structure to effectively support and oppose those heaps. The heaps can act naturally weight of the structures, other dead load, live loads, moving (wheel) stack, wind stack, tremor stack, stack from temperature change and so forth. The structural designer must outline structures to be safe for their clients and to effectively satisfy the capacity they are intended for (to be useful). Because of the idea of some stacking conditions, sub-teaches inside structural engineering have risen, including wind engineering and seismic tremor engineering.
Design considerations will incorporate quality, firmness, and strength of the structure when subjected to loads which might be static, for example, furniture or self-weight, or dynamic, for example, wind, seismic, group or vehicle loads, or momentary, for example, transitory development loads or effect. Different considerations incorporate cost, constructability, safety, style and sustainability.
- Energy efficiency in buildings
- Green building materials
- Earthquake engineering
- Bridge engineering
- Structural health monitoring
- Special concrete
- Management of infrastructure construction
- Computational Mechanics
Track 3: Building Technology and Construction Management
The Building Technology and Construction Management division functions as a center of teaching, learning, and research in Building Physics, Concrete Technology, and Construction Management. Construction usually refers to the erection of large structures such as buildings, ship, aircraft, dams, roads, and bridges. By extension, Construction Technology Management refers to the planning, coordination and successful implementation of such structures. A branch of Civil Engineering, Construction Technology and Management is a fusion of civil engineering and construction management which may incorporate the principles of drainage, water supply and distribution, heating and ventilation, and recycling of construction and demolition waste management.
- Computational laboratory for construction management
- Construction and contract management
- Construction engineering practices
- Construction methods and equipment
- Design of structures
- Heavy equipment operations
Track 4: Steel Structures and Construction
Structural steel is a classification of steel utilized for making development materials in an assortment of shapes. Numerous structural steel shapes appear as a lengthened bar having a profile of a particular cross segment. Structural steel shapes, sizes, synthetic arrangement, mechanical properties, for example, qualities, stockpiling rehearses, and so on, are directed by guidelines in most industrialized nations. Most structural steel shapes, for example, I-pillars, have high second snapshots of territory, which implies they are hardened in regard to their cross-sectional region and consequently can bolster a high load without inordinate hanging.

Steel Construction is the development of a metal structure created with steel for the internal support and for exterior. Advantages are there of utilizing steel are steel is cost effective, energy efficient product which does not simply warp, buckle, twist or bend, and is therefore easy to modify and offers design flexibility.
- High Performance basic steel
- Material Quality & Control
- Cold formed steel
- Non-structured steel
- Future trends in steel structures
- Advanced sustainable material
- Sustainable steel structure
- Composite construction
Track 5: Structural Analysis and Designing
Structural analysis is done by an examination of the genuine structure, on a model of the structure made on some scale, and by the use of numerical models. Tests are directed on the genuine structure when creation is expected of comparable structures in expansive amounts, similar to edges of a specific auto, or when the test costs are satisfactory because of the noteworthiness of the assignment. At the point when components of the primary structures are to be inspected, at that point models are utilized for the estimation of the diverse burdens to be persevered. Most auxiliary investigations are directed on the scientific models, in which the model could be flexible or inelastic, powers might be static or dynamic, and the model of the structure may be two dimensional or three dimensional. Structural analysis is an essential subject of structural designing that assesses the distinctive loads on structures, and their effects. It is an exact technique to learn the ability of the structures to withstand the normal loads, and help with planning the structures in like manner.
- Structures and Loads
- Classification of structures
- Analytical methods and Limitations
- Strength of materials methods
- Elasticity methods
- Methods using numerical approximation
Track 6: Structural Health Monitoring
Structural health monitoring (SHM) alludes to the way toward executing a damage detection and portrayal technique for designing structures. Here damage is characterized as changes to the material or potentially geometric properties of a structural framework, including changes to the limit conditions and framework availability, which adversely influence the framework's execution. The SHM procedure includes the perception of a framework after some time utilizing intermittently tested dynamic reaction estimations from a variety of sensors, the extraction of harm delicate highlights from these estimations, and the factual examination of these highlights to decide the present condition of framework health. For long term SHM, the yield of this procedure is intermittently refreshed data with respect to the capacity of the structure to play out its expected capacity in light of the inescapable maturing and degradation coming about because of operational conditions. After extraordinary occasions, for example, seismic tremors or impact stacking, SHM is utilized for quick condition screening and intends to give, in close constant, solid data with respect to the uprightness of the structure. Foundation investigation assumes a key job out in the open wellbeing with respect to both long haul harm amassing and post extraordinary occasion situations. As a feature of the quick improvements in information driven advances that are changing numerous fields in building and science, machine learning and PC vision methods are progressively prepared to do dependably diagnosing and arranging designs in picture information, which has clear applications in review settings.
- Statistical pattern recognition
- Health assessment of engineered structures
- Operational evaluation
- Data acquisition, normalization and cleansing
- Feature extraction and data compression
- Statistical model development
Track 7: Reinforced Concrete Structure
Reinforced concrete is the concrete in which steel is inserted in such a way, to the point that the two materials act together in opposing powers. The reinforcing steel—bars, bars, or work—ingests the tractable, shear, and now and again the compressive stresses in a concrete structure. Plain concrete does not effectively withstand ductile and shear stresses caused by wind, tremors, vibrations, and different powers and are in this way inadmissible in most basic applications. In reinforced concrete, the rigidity of steel and the compressive quality of concrete cooperate to enable the part to manage these stresses over significant ranges.

The innovation of reinforced concrete in the nineteenth century altered the development business, and concrete wound up one of the world's most normal building materials.
- Mechanism of composite action of reinforcement and concrete
- Anchorage (bond) in concrete: Codes of specifications
- Anti-corrosion measures
- Reinforcement beams
- Prestressed concrete
- Common failure modes of steel reinforced concrete
- Steel plate construction
- Fiber-reinforced concrete
- Non-steel reinforcement
Track 8: Modular Constructions
Modular construction is a term used to portray the utilization of processing plant created pre-designed building units that are conveyed to site and collected as huge volumetric parts or as generous components of a building. The modular units may frame finish rooms, parts of rooms, or separate much adjusted units, for example, toilets or lifts.

The accumulation of discrete modular units more often than not shapes a self-supporting structure in its own particular right or, for tall structures, may depend on an autonomous basic system.
The main sectors of application of modular construction are:
- Private housing
- Social housing
- Apartments and mixed use buildings
- Educational sector and student residences
- Key worker accommodation and sheltered housing
- Public sector buildings, such as prisons and MoD buildings
- Health sector buildings
- Hotels
Track 9: Earthquake Engineering and Seismic Risk Mitigation
Earthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that outlines and examinations structures, for example, buildings and bridges, in view of earthquakes. Its general objective is to make such structures more impervious to earthquakes. An earthquake (or seismic) build means to develop structures that won't be harmed in minor shaking and will stay away from genuine harm or crumple in a noteworthy earthquake. Earthquake engineering is the logical field worried about securing society, the indigenous habitat, and the man-made condition from earthquakes by constraining the seismic hazard to socio-monetarily worthy levels. Customarily, it has been barely characterized as the investigation of the conduct of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic stacking; it is considered as a subset of structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, applied physics, and so on.

In any case, the tremendous costs experienced in late earthquakes have prompted a development of its extension to include disciplines from the more extensive field of structural engineering, mechanical engineering and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics and finance.
- Advanced Structures
- Integrating Science into Disaster Risk Reduction
- Natural and Environmental Disasters
- Finite Element Modelling and Numerical Methods
- Design & Analysis of Structural Systems
- Catastrophe Risk Modelling
- Earthquake Seismology and Earthquake Hazard
- Project Management
Track 10: Transportation and Traffic Engineering
Traffic engineering is a part of civil engineering that utilizes engineering techniques to accomplish the sheltered and productive development of individuals and merchandise on roadways. It focuses essentially around research for sheltered and effective traffic stream, for example, road geometry, sidewalks and crosswalks, cycling infrastructure, traffic signs, road surface markings and traffic lights. Traffic engineering manages the functional part of transportation framework, aside from the infrastructures provides.

The design parts of transport engineering includes the estimation of transportation facilities (what number of paths or how much capacity the facilities has), deciding the materials and thickness utilized in pavement, designing the geometry (vertical and level arrangement) of the roadway (or track). Operations and management include movement engineering, with the goal that vehicles move easily on the road or track. Older techniques include signs, signals, markings, and tolling. Fresher innovations include intelligent transportation systems, including propelled explorer information systems, such as variable message signs), advanced traffic control systems (such as ramp meters), and vehicle infrastructure integration. Human components are a part of transport engineering, especially concerning driver-vehicle interface and user interface of road signs, signals, and markings.
- Port and harbor engineering
- Airport engineering
- Pavement engineering
- Bicycle transportation engineering
- Highway engineering
- Transportation planning
- Urban planning
- Human factors engineering
Track 11: Pavement Design
A highway pavement is a structure comprising of superimposed layers of handled materials over the common soil sub-review, whose primary function is to convey the connected vehicle burdens to the sub-review. The pavement structure ought to have the capacity to give a surface of satisfactory riding quality, sufficient slip opposition, great light reflecting characteristics, and low commotion contamination. A definitive point is to guarantee that the transmitted stresses because of wheel load are adequately diminished, so that they will not exceed bearing capacity of the subgrade.
Two sorts of pavements are by and large perceived as filling this need, specifically Flexible pavements and Rigid pavements. Improper design of pavements prompts early failures of pavements influencing the riding quality.
- Flexible pavements
- Rigid pavements
- Characterization of bituminous binders and mixtures
- Advances in bituminous pavement and construction
- Advances in concrete pavement construction
- Bituminous pavement design
- Cold and warm mix technology
- Pavement management systems
- Traffic management systems
Track 12: Environmental Engineering
Environmental engineering is the branch of engineering that is worried about shielding individuals from the impacts of unfavourable environmental impacts, for example, contamination, and additionally enhancing environmental quality. Environmental specialists work to enhance reusing, squander transfer, general wellbeing, and water and air contamination control.

- Ecological engineering
- Fire protection engineering
- Sanitary engineering
- Wastewater engineering
- Advanced technologies in water and waste water treatment
- Biomass energy technologies
Track 13: Water Resource Engineering and Technology
Water resources engineering and technology experts study and make recommendations on new water treatment facilities, reactors, pumping stations, waste frameworks and pipelines. Water resources engineering and technology is an area of study within the engineering sciences managing the hydraulic and fluid mechanics standards behind water distribution, flow and manipulation.

Water resources engineers outline and actualize water frameworks. The design may focus around hydraulics, pipelines and research facility tests, while the execution may deal with flood damage, wastewater transfer and consumable water distribution, potable water distribution and reclamation, environmental change examination, aquifer stockpiling and recuperation and surface/groundwater connection.
- Hydraulic engineering
- River engineering
- Coastal engineering
- Groundwater engineering
- Water Resources Planning and management
Track 14: Geotechnical Engineering
Geotechnical Engineering is a part of structural engineering worried about the engineering behavior of earth materials. Geotechnical engineering incorporates researching existing subsurface conditions and materials; surveying dangers presented by site conditions; designing earthworks and structure foundations; and monitoring site conditions, earthwork and establishment construction.

A typical geotechnical engineering project starts with a site investigation of soil and bedrock on and underneath a zone. Investigations can incorporate the evaluation of the hazard to humans, property and the earth from common perils, for example, earthquakes, landslides, sinkholes, soil liquefaction, debris flows and rock falls. Foundations are outlined and built for structures of different sizes, for example, elevated structures, bridges, medium to huge business buildings, and littler structures where the soil conditions don't permit code-based plan. Foundations worked for over the ground structures incorporate shallow and profound foundations. Holding structures incorporate earth-filled dams and holding walls. Earthworks incorporate banks, burrows, levees, channels, repositories, testimony of dangerous waste and sterile landfills.
Geotechnical engineering is additionally identified with coastal and ocean engineering. Coastal engineering can include the plan and construction of wharves, marinas, and jetties. Ocean engineering can include establishment and stay frameworks for offshore structures, for example, oil stages.
- Soil mechanics
- Uncertainties, risk and reliability geotechnical engineering
- Geo-environmental engineering
- Forensic geotechnical engineering
- Sustainable geotechnics
- Geosynthetics
- Retrofitting strategies for geotechnical structures
- Computational geomechanics and geotechnical modelling
- Geohazrds: Analysis, mitigation and management
Track 15: Sustainability & Green Structures
Green building (otherwise called green construction or sustainable building) alludes to both a structure and the use of procedures that are environmentally dependable and asset effective all through a building's life-cycle: from planning to outline, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractual worker, the designers, the architects, and the customer at all task stages. The Green Building practice expands and supplements the established building configuration worries of economy, utility, durability, and comfort.

Some of the more common green construction practices include:
- Using sustainable building materials like recycled glass and steel, as well as renewable materials like bamboo and rubber;
- Installing energy-efficient windows and doors;
- Using lower-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints and stains;
- Constructing green roof systems (aka “plants on your roof”) that offer many benefits, including onsite gardens, rainwater management and protection from the effects of harmful UV light;
- Adding water harvesting and purification systems that don’t just manage, but also make the most use of rainfall;
- Maximizing natural light, which cannot only save on lighting requirements (and subsequently energy costs), but can also help keep buildings warm in colder months; and
- Using renewable energy to power the building: for example, installing a commercial solar panel system.
- Life cycle assessment
- Siting and structure design efficiency
- Energy efficiency
- Water efficiency
- Materials efficiency
- Indoor environmental quality enhancement
- Operations and maintenance optimization
- Waste reduction
- Reduce impact onto electricity network
Track 16: Materials Science and Engineering
Materials science is firmly identified with civil engineering. It examines crucial qualities of materials, and manages earthenware production, for example, cement and blend black-top concrete, solid metals, for example, aluminum and steel, and thermosetting polymers including polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) and carbon fibers. Materials engineering includes protection and prevention (paints and wraps up). Alloying joins two kinds of metals to create another metal with wanted properties. It consolidates components of connected material science and science. With late media consideration on nanoscience and nanotechnology, materials engineering has been at the bleeding edge of academic research. It is additionally a vital piece of forensic engineering and failure analysis.
- Nanomaterials
- Biomaterials
- Electronic, optical, and magnetic
- Computational science and theory
Track 17: Tunnel Engineering and Construction
Tunnels are dug in sorts of materials fluctuating from delicate mud to hard shake. The technique for burrow development relies upon such factors as the ground conditions, the ground water conditions, the length and distance across of the passage drive, the profundity of the passage, the coordination of supporting the passage removal, the last utilize and state of the passage and proper hazard administration.

There are three fundamental kinds of tunnel construction in common use:
- Cut-and-cover tunnel (constructed in a shallow trench and then covered over)
- Bored tunnel, constructed in situ, without removing the ground above. They are usually of circular or horseshoe cross-section.
- Immersed tube tunnel, sunk into a body of water and laid on or buried just under its bed.
- Geotechnical investigation and design
- Choice of tunnels versus bridges
- Project planning and cost estimates
- Sprayed concrete techniques
Track 18: Automation in Construction
The construction business is one of the largest industries in the world, despite its tremendous potential; many firms are struggling due to a shortage of skilled workers, weak productivity growth, and new data showing that the industry generates immense waste, both in terms of human productivity and physical materials. Today’s proponents of technology have pointed to a lack of automation and adoption of technology as the primary reasons for the industry’s poor performance – construction is one of the least digitized industries worldwide, and has resultantly failed to significantly increase worker productivity in decades.

The effective use of automation is one of the greatest opportunities, as well as one of the greatest challenges, facing the construction industry. The major components of an automation strategy, as considered in this paper, are computer-aided engineering and design (CAE/CAD), computerized data bases, feedback of as-built data, automated materials handling, artificial intelligence, and robotics.
- Drones Used to Conduct Site Inspections
- Monitor Inventory
- Automation of Prefabricated Home Construction
- Artificial intelligence
Track 19: Designing of Special Structures and Concrete Technology
Concrete Technology focuses on concrete making materials including supplementary cementitious materials. Concrete generation process additionally forms a piece of the discourse. Experiencing the course one would grow direct learning on concrete generation process and properties and employments of concrete as a cutting edge material of development. This technology empowers one to settle on proper choice with respect to fixing choice and utilization of concrete.

Strengthened cement is a composite material in which cement's by and large low solidness and pliability are killed by the mix of fortification having higher flexibility or versatility. The fortress is ordinarily, anyway not by any stretch of the creative ability, Steel reinforcing bars (rebar) and is for the most part inserted idly in the solid before the solid sets. Managing outlines are all around wanted to limit malleable anxieties especially region of the solid that may cause prohibited breaking and furthermore partner disappointment. Present day strengthened cement can contain swayed supporting materials made of Steel, polymers or substitute composite material related to rebar or not. Strengthened cement may in like way be forever worried (in weight), to overhaul the direct of the last structure under working weights. In the United States, the most comprehensively saw frameworks for doing this are known as pre-tensioning and post-tensioning.
- Design of Silos
- Design Retaining Wall
- Design RC Wall Tanks
- Analysis of wind Loads
- Grades and strength of concrete
Track 20: Construction Market Research and Industry Analysis
Construction, in the sense of architectural and civil engineering, is the building of real property. The worldwide construction industry represents a few trillion dollars. Given the measure of the market and its prospects for further extension, the construction business speaks to an alluring open door for material suppliers and segment suppliers. Basic to accomplishment in the construction business is learning of market patterns, item blend shifts, client needs and viable market procedures. Our ceaseless networking with clients, suppliers and competitors creates complete visibility across the whole value chain of the construction industry and enables our clients to settle on sure business choices. Keeping in mind the end goal to finish a construction project, a scope of variables must be considered, including planning, logistics, wellbeing of the construction site, building materials, public inconvenience, and environmental impact and scheduling. Different elements that ought to be considered are budgetary, design and legitimate issues, particularly since there's dependably the likelihood of a negative result amid a construction project, for example, basic fall and cost overwhelms. Other than contractual workers, different gatherings of professionals can meet up to perform construction work, including project managers, construction engineers, design engineers, project architects, logistics professionals, construction managers, plumbers, surveyors, electricians, laborers and skilled workers.
- Strategic Growth Consulting
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Due Diligence
- Capital Investment Analysis
- Opportunity Screening and Analysis
- Market Entry Strategy
- Target Screening
- Customer Experience
Market Analysis
The global civil engineering market size was valued at USD 7.84 trillion in 2017 and is expected to register a CAGR of 5.6% from 2018 to 2025. The market is anticipated to be driven by an expanding residential sector in the emerging economies of Asia Pacific. Rapidly rising urban population, coupled with growing need to accommodate them is a key factor boosting this market. Ongoing infrastructural development has also favored the market, along with strict government regulations and rise in international investments in developing regions such as Asia Pacific and Middle East and Africa (MEA).
Global civil engineering market size, by service (2013-2025):
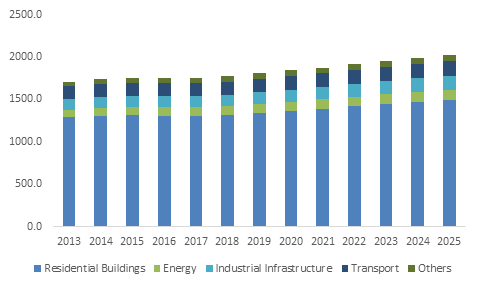
Regulations in Europe and North America regarding volatile organic compounds (VOC) emissions during construction processes is expected to boost demand for precast/prefabricated construction products in these regions. Companies involved in civil engineering all over the world are increasingly focusing on green building products thanks to growing awareness about the importance of eco-friendly products and energy efficiency. Introduction of new materials and technologies is expected to create lucrative opportunities for players over the next few years.
Various government regulatory frameworks, such as the International Building Code (IBC), are applied to new and existing buildings in order to track and register specific infrastructure w.r.t. government processes and control illegal and unethical construction practices.
Global civil engineering market share, by application (2017) in % (percentage):
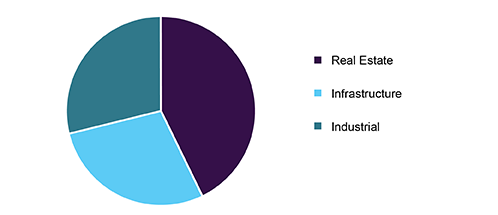
The construction sector is a key segment within the market, driven largely by booming building and construction activities in Asia Pacific and MEA. This is supported by various international companies and associated service providers investing in these regions. India, China, Saudi Arabia, UAE, and other developing countries are expected to show significant growth in infrastructural development during the forecast period. Civil engineering is one of the most prominent and vital elements in regional development. Infrastructural development significantly depicts potential growth possibilities of any regions.
Learn More
Civil Engineering Universities in Europe
Kingston University, England|University of Manchester, England|University of Aberdeen School of Engineering, Scotland|Anglia Ruskin University, England|University of Birmingham, England|University of Brighton, England|Brunel University London, England|Coventry University, England|University of Edinburgh, Scotland|Hanze University of Applied Sciences, Groningen, The Netherlands|Heriot-Watt University, Scotland|Lancaster University, England|Swansea University, Wales|University of Westminster, London|Aalborg University, Denmark|Antalya International University, Turkey|University of Bologna, Italy|Brno University of Technology, Czech Republic|Cork Institute of Technology, Republic of Ireland|Dresden University of Technology (TUD), Germany|Trinity College Dublin, Republic of Ireland|Ecole Centrale De Nantes, France|Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences, Finland|University of Liège, Belgium|University of Maribor, Slovenia|Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Norway
Civil Engineering Universities in USA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), United States|Virginia Tech, Blacksburg|Stanford University, Stanford|University of Texas, Austin|Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta|University of California, Berkeley|University of Illinois- Urbana-Champaign, Urbana|Purdue University- West Lafayette|Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh|Cornell University, Ithaca|Eastern Michigan University, Ypsilanti, USA|Bowling Green State University, Bowling Green, USA|University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, USA|Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, USA|Stanford University, Stanford, USA|California State University Los Angeles Campus, Los Angeles|New York University, New York, USA|Texas A & M University, College Station, USA|The University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, USA|University of California (Los Angeles Campus), Los Angeles, USA|University of California (Berkeley Campus), Berkeley, USA|Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA|California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA|Georgia Institute of Technology , Atlanta, USA|California State University Long Beach, Los Angeles, USA|Northeastern University , Boston, USA|Texas A&M University–Kingsville, Kingsville, USA|New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, USA
Civil Engineering Universities in Asia
The University of Tokyo, Japan|National University of Singapore (NUS), Singapore|Tsinghua University, China|Kyoto University, Japan|Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan|KAIST – Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea|Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore|The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), Hong Kong|Seoul National University (SNU), South Korea|Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China|Peking University, China|National Taiwan University (NTU), Taiwan|University of Hong Kong (HKU), Hong Kong|Tohoku University, Japan|Osaka University, Japan|Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB), India|Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IITD), India|Zhejiang University, China|Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), India|The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK), Hong Kong|Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), South Korea|Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (IITK), India|University of Science and Technology of China, China|The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong|Indian Institute of Science, India|National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan|Nagoya University, Japan|Harbin Institute of Technology, China|Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur (IITKGP), India|Korea University, South Korea|Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee (IITR), India
Top Companies Associated with Civil Engineering
- LEIGHTON
- STRABAG
- SNC-Lavalin
- HOCHTIEF
- TAISEI Corporation
- Murray & Roberts
- AECOM Technology Corp., Los Angeles
- Jacobs Engineering Group
- URS Corporation
- HDR, Inc.
- AECOM Technology Corporation
Major Societies and Associations around the Globe
- American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE)
- Institution of Civil Engineers
- The Institution of Civil Engineering Surveyors
- Institution of Engineers of Ireland
- Institute of Transportation Engineers
- Transportation Research Board
- European Association for Structural Dynamics
- American Association of Engineering Societies
- Canadian Society for Civil Engineering
- Earthquake Engineering Research Institute
- Engineers Australia
- European Federation of National Engineering Associations
- International Federation of Consulting Engineers
- Indian Geotechnical Society
- Institution of Structural Engineers
- International Society of Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering
- Institution of Engineers (India)
- Civil Engineers
- Structural Engineers
- Civil Industry Professionals
- Building Services Engineer
- Building Control Surveyor
- Environmental Engineers
- Bridge Construction Industries
- Renewable Energy Industries
- Earthquake Engineering Research Institutes
- Institutions of Civil Engineering Surveyor
Software used in Civil Engineering
- POLYBEAM: A Simple Beam Calculator
- ENGILAB UNITS: Units Conversion Tool
- TIMBERTECH BUILDINGS: Structural Analysis and Design of Timber Structures
- ANALYSIS3D: Finite Element Analysis Package for 2D and 3D Constructions
- SO-SIEVE: Sieve Analysis, Hydrometer and Atterberg Limits Tests
- WINTOPO: Raster to Vector Converter
- SITE3D: Site and Road Engineering 3D Design
- ELLEA1: Pavement Analysis Tool
- STRUCTURAL TIMBER DESIGNER: Design Of Wooden Structures
- ADONIS: Two-Dimensional Geotechnical Finite Element Program
- SO-LOG: Geotechnical Engineering Boring Logs
- RSPILE: Pile Capacity Analysis
- Building Information Modeling
- AutoCAD Civil 3D
- SAP 2000
- Project management software
- HEC-RAS
- Micro Station
- ETABS
- World Congress on Construction and Steel Structure | November 16-18, 2015 Dubai, UAE
- Sustainable Civil Engineering | June 23-25, 2016 Cape Town, South Africa
- 2nd Global Geologists Annual Meeting | July 21-22, 2016 Brisbane, Australia
- International Conference on Recent Researches in Engineering, Science and Technology Salem, India
- IASTEM - The 2nd International Conference on Civil and Architectural Engineering(ICCAE) Singapore
- 3rd International Conference on Rehabilitation and Maintenance in Civil Engineering Solo, Indonesia
- 3rd International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering (I2C2E) Berlin, Germany
- International Summit on Conventional and Sustainable Energies | March 30-31, 2018 | Orlando, USA
- 4th International Conference and Business Expo on Wireless, Telecommunication & IoT | May 28-29, 2018 | London, UK
- International Summit and Expo on Optical Fibre Communications | May 30-31 2018 | Auckland, Newzealand
- 9th Euro Biosensors & Bioelectronics Congress | September 13-14, 2018 | London, UK
- 2nd World Congress on Wind & Renewable Energy | June 14-15, 2018 | London, UK
Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering | Journal of Material Sciences & Engineering | Journal of Architectural Engineering Technology | Journal of Applied Mechanical Engineering | Journal of Aeronautics & Aerospace Engineering | Methodology of Classifying the Causes of Occupational Accidents Involving Construction Scaffolding Using Pareto-Lorenz Analysis | Sustainable Decision-Making in Civil Engineering | Construction and Building Technology | Tsallis Entropy Theory for Modeling in Water Engineering: A Review | An Integrated Numerical Model for the Design of Coastal Protection Structures | Effect of Nano-CuO on Engineering and Microstructure Properties of Fibre-Reinforced Mortars Incorporating Metakaolin: Experimental and Numerical Studies | Finite Element Analysis of Grouting Compactness Monitoring in a Post-Tensioning Tendon Duct Using Piezoceramic Transducers | How to Align the University Curricula with the Market Demands by Developing Employability Skills in the Civil Engineering Sector | The Gigantism of Public Works in China in the Twenty-First Century | Nonlinear Modelling of Curved Masonry Structures after Seismic Retrofit through FRP Reinforcing | Experimental Investigation of Debris-Induced Loading in Tsunami-Like Flood Events | Analysis of Cylindrical Granular Material Silos under Seismic Excitation | Using Acoustic Emission Methods to Monitor Cement Composites during Setting and Hardening | Measurement of the Length of Installed Rock Bolt Based on Stress Wave Reflection by Using a Giant Magnetostrictive (GMS) Actuator and a PZT Sensor | Nanocarbons in Electrospun Polymeric Nanomats for Tissue Engineering: A Review | A Helicopter View of the Special Issue on Wave Energy Converters | A Two-Step Strategy for System Identification of Civil Structures for Structural Health Monitoring Using Wavelet Transform and Genetic Algorithms | Wind-Induced Fatigue Analysis of High-Rise Steel Structures Using Equivalent Structural Stress Method | Urban Resilience: A Civil Engineering Perspective | Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties and Porosity of Organic Microcapsules Based Self-Healing Cementitious Composite | Impedance-Based Non-Destructive Testing Method Combined with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Structural Health Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures | Tapered Polymer Fiber Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Beam Vibration Detection | Strain Rate Behavior in Tension of Reinforcing Steels HPB235, HRB335, HRB400, and HRB500 | Enhancing the Hydrophilicity and Cell Attachment of 3D Printed PCL/Graphene Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering | Microstructure-Based Prediction of the Elastic Behaviour of Hydrating Cement Pastes | Assessment of Changes in Flood Frequency Due to the Effects of Climate Change: Implications for Engineering Design | An Experimental Study of a Data Compression Technology-Based Intelligent Data Acquisition (IDAQ) System for Structural Health Monitoring of a Long-Span Bridge | Study of Impact Damage in PVA-ECC Beam under Low-Velocity Impact Loading Using Piezoceramic Transducers and PVDF Thin-Film Transducers | Modelling Geotechnical Heterogeneities Using Geostatistical Simulation and Finite Differences Analysis | Engineering Properties of Self-Consolidating Lightweight Aggregate Concrete and Its Application in Prestressed Concrete Members | Effect of Aggregate Mineralogy and Concrete Microstructure on Thermal Expansion and Strength Properties of Concrete | A System-of-Systems Approach for Integrated Resilience Assessment in Highway Transportation Infrastructure Investment | Research on the Rational Yield Ratio of Isolation System and Its Application to the Design of Seismically Isolated Reinforced Concrete Frame-Core Tube Tall Buildings | Output-Based Structural Damage Detection by Using Correlation Analysis Together with Transmissibility | Toughness of Railroad Concrete Crossties with Holes and Web Openings | The Use of CFD in the Analysis of Wave Loadings Acting on Seawave Slot-Cone Generators | Deep Tunnel for Regulating Combined Sewer | Overflow Pollution and Flood Disaster: A Case Study in Guangzhou City, China | Development of a Tomography Technique for Assessment of the Material Condition of Concrete Using Optimized | Elastic Wave Parameters | The Influence of Hydrologic Parameters on the Hydraulic Efficiency of an Extensive Green Roof in Mediterranean Area | Flexural Strengthening of RC Slabs with Prestressed CFRP Strips Using Different Anchorage Systems | Engineering Behavior and Characteristics of Wood Ash and Sugarcane Bagasse Ash | Critical Data Source; Tool or Even Infrastructure? Challenges of Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing for Disaster Risk Governance | Properties of Cement Mortar by Use of Hot-Melt Polyamides as Substitute for Fine Aggregate | Virtual Placements to Develop Employability Skills for Civil and Environmental Engineering Students | Durability Indicators Comparison for SCC and CC in Tropical Coastal Environments | Effects of Biosolids and Manure Application on Microbial Water Quality in Rural Areas in the US | Feasibility of Frequency-Modulated Wireless Transmission for a Multi-Purpose MEMS-Based Accelerometer | Functionality Enhancement of Industrialized Optical Fiber Sensors and System Developed for Full-Scale Pavement Monitoring | Balancing Power Output and Structural Fatigue of Wave Energy Converters by Means of Control Strategies | A Wireless Fatigue Monitoring System Utilizing a Bio-Inspired Tree Ring Data Tracking Technique | The SSG Wave Energy Converter: Performance, Status and Recent Developments | Human Health Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals in Water: Issues and Challenges Ahead.
The Total Risk Analysis of Large Dams under Flood Hazards | Long-Term Downstream Effects of a Dam on a Lowland River Flow Regime: Case Study of the Upper Narew | Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change on River Discharge Dynamics in Oueme River Basin (Benin, West Africa) | A Comparison of the Energy Saving and Carbon Reduction Performance between Reinforced Concrete and Cross-Laminated Timber Structures in Residential Buildings in the Severe Cold Region of China | Influence of Parameter Sensitivity and Uncertainty on Projected Runoff in the Upper Niger Basin under a Changing Climate | Impacts of Climate Change on the Hydrological Regime of the Danube River and Its Tributaries Using an Ensemble of Climate Scenarios | Improving Hydro-Climatic Projections with Bias-Correction in Sahelian Niger Basin, West Africa | Multi-Basin Modelling of Future Hydrological Fluxes in the Indian Subcontinent | Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Reservoir Inflows Using Multi Climate-Models under RCPs—The Case of Mangla Dam in Pakistan | Coupling Land Use Change Modeling with Climate Projections to Estimate Seasonal Variability in Runoff from an Urbanizing Catchment Near Cincinnati, Ohio| Assessing the Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Value Uncertainty to Extreme Flows across Great Britain | Hydrological Appraisal of Climate Change Impacts on the Water Resources of the Xijiang Basin, South China | Assessing River Low-Flow Uncertainties Related to Hydrological Model Calibration and Structure under Climate Change Conditions | Mean Normalized Force Computation for Different Types of Obstacles due to Dam Break Using Statistical Techniques | Case Study: Effects of a Partial-Debris Dam on Riverbank Erosion in the Parlung Tsangpo River, China | A Multi-Faceted Debris-Flood Hazard Assessment for Cougar Creek, Alberta, Canada| Study on the Formation and Initial Transport for Non-Homogeneous Debris Flow | Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams | Share your Insights and Learn How Readers Discover Content | Seismic Responses of a Cable-Stayed Bridge with Consideration of Uniform Temperature Load | Parallel Dynamic Analysis of a Large-Scale Water Conveyance Tunnel under Seismic Excitation Using ALE Finite-Element Method | A New Finite Element Formulation for Nonlinear Vibration Analysis of the Hard-Coating Cylindrical Shell | 3D FE Analysis of RC Beams Externally Strengthened with SRG/SRP Systems | An Asymptotic Theory for the Nonlinear Analysis of Laminated Cylindrical Shells | Thermoelectrically induced nonlinear free vibration analysis of piezo laminated composite conical shell panel with random fiber orientation | The influence of triggers geometry upon the stiffness of cylindrical thin walled tubes | Buckling Analysis of 3D Braided Composite Cylindrical Shells under Axial Loads | Acoustic Emission Behavior of Early Age Concrete Monitored by Embedded Sensors | A New Fault Location Approach for Acoustic Emission Techniques in Wind Turbines | Transverse Crack Detection in 3D Angle Interlock Glass Fibre Composites Using Acoustic Emission | Non-Destructive Evaluation for Corrosion Monitoring in Concrete: A Review and Capability of Acoustic Emission Technique | Detection of failures of adhesively bonded joints using the acoustic emission method | Wood-cement inhibition revisited and development of new wood-cement inhibitory and compatibility indices based on twelve wood species | Functionalization of Sol-Gel Zirconia Composites with Europium Complexes | Mechanical Properties of Sandy Soil Improved with Cement and Nanosilica | Development of a Novel Guided Wave Generation System Using a Giant Magnetostrictive Actuator for Nondestructive Evaluation | Monitoring of Pre-Load on Rock Bolt Using Piezoceramic-Transducer Enabled Time Reversal Method | Monitoring of Grouting Compactness in a Post-Tensioning Tendon Duct Using Piezoceramic Transducers
Recycled aggregates; Construction and demolition waste; Thermal performance; Thermal conductivity; Nanofiltration; Tight ultrafiltration; Concentration Polarization; Fouling; Natural organic matter; Shredded EPDM rubber; Roof membrane; Lightweight fill; Retaining wall backfill; Strain transfer analysis; Clamped fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensor; Shear-lag theory; Gauge ratio; Interlayer thickness; Strain transfer analysis; Shear-lag theory; Gauge Ratio; Interlayer thickness; System Engineering; Project governance; Quality assurance; Civil protection; Emergency management; Augmented reality; Crowd-mapping; Social networks; Sensor networks; Geomatics; Hydrogeology; Concrete sleeper; Crosstie; Design standard; Holes; Web opening; Railway infrastructure; Static performance; CFD modeling; Physical modeling; Wave forces; Wave pressures; Combined Sewer Overflow pollution; Deep Tunnel Engineering; DongHaoChong basin; Flood disaster; SWMM model; Tomography; Honeycomb; Pre-stressed concrete (PC); Imaging algorithm; Ray tracing; Wave propagation; Stormwater management; Green roof; Rainfall-runoff; Retention; Inter-event time; RC plate strengthening; CFRP strips; Prestressing; Mechanical anchorage; Gradient anchorage; Static loading tests; Cross-section analysis; Numerical Simulations; Biomass; Wood ash; Sugarcane bagasse ash; Characterization; Disaster Risk Management; Geographic information systems; Remote Sensing;Volunteered Geographic Information; Crowdsourcing; Critical infrastructure; Crisis mapping; Civil protection; Hot-melt polyamide; Heat treatment; Self-repairing; Hot-melt polyamide (HMP)/cement composite system; Physical adhesion; Self-compacting concrete (SCC); Conventional vibrated concrete (CC); Durability; Best management practices; Biosolids; Manure; Contamination of ground and surface waters; Microbial source tracking; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Risk assessment; Rural systems; Waterborne diseases; Water quality; Acceleration measurement; MEMS sensor; Prototype; Structural health monitoring; Vibration measurement; Voltage to frequency conversion; Wireless accelerometer; Pavements; Functionality enhancement of industrialized optical fiber sensors; Self-healing network system; Full-scale monitoring; Fatigue; Structural health monitoring (SHM); Rain-flow counting method; Data tracking of tree rings; Digital Signal Processing (DSP); Wireless sensor; PVDF; Wave Energy Converters; Wave energy; Wave basin experiments; WEC arrays/farms/parks; Point absorber; DHI shallow water wave Basin; Wave energy converter; Overtopping; SSG; Model tests; Human health; Pharmaceuticals; Mixture Toxicity; Risk Assessment; Uncertainty; Engineering Education; Interrelationships between people; Resources; Environment and development; Hands-on projects; Humanitarian development
































